选择合适的传感器其实很简单:你只需要知道测量什么量,大致的测量范围是什么?
Choosing the right sensor is actually very simple: you just need to know what quantity to measure and what is the approximate measurement range?
当你找到了这两个问题的答案后,还有几个方面需要考虑,包括:传感器的负载限制,可允许的负荷,需要特殊考虑的方面,以及如何做出合理的评估。
Once you've found the answers to these two questions, there are several more aspects to consider, including: the sensor's load limits, allowable loads, areas that require special consideration, and how to make a reasonable assessment.

技术参数表规范及其关系
当查看扭矩传感器技术参数表时,您会发现有最大允许载荷、力矩或要遵守标准的详细信息。数据可能因制造商或类型而异。然而,在寻找最适合的扭矩传感器时,标准始终起着决定性的作用。
When looking at the torque transducer data sheet, you will find details of the maximum permissible load, torque or standard to be complied with. Data may vary by manufacturer or type. However, when it comes to finding the most suitable torque transducer, the standard always plays a decisive role.
仔细查看这些参数时,您会发现一些需要解释的相关术语:
When you take a closer look at these parameters, you'll find some relevant terms that need to be explained:
额定力/额定扭矩 Rated force/rated torque
极限载荷/极限扭矩 Ultimate load/ultimate torque
破坏载荷/扭矩 Breaking load/torque
负载率总和 Load Rate Sum (LRS)
静态载荷 Static load
理解各个术语之间如何关联的最好的方法是考虑哪些负载可以发生,以及如何对它们进行分类。在应用中,除此处所示的机械载荷外,还应考虑其他载荷,例如由温度或其他环境影响而产生的载荷。然而,在大多数情况下,这是没有必要的,或者在有疑问的情况下,可以快速识别判断。无论我们谈论的是单轴还是多轴、静态还是动态、脉动还是交变负载,都应该采用一些测试标准来确保传感器的安全运行。
The best way to understand how the terms relate to each other is to consider which loads can occur and how to classify them. In the application, in addition to the mechanical loads shown here, other loads, such as those arising from temperature or other environmental influences, should also be considered. However, in most cases, this is not necessary, or in case of doubt, a quick identification judgment can be made. Whether we are talking about single-axis or multi-axis, static or dynamic, pulsating or alternating loads, there are test criteria that should be applied to ensure the safe operation of the sensor.
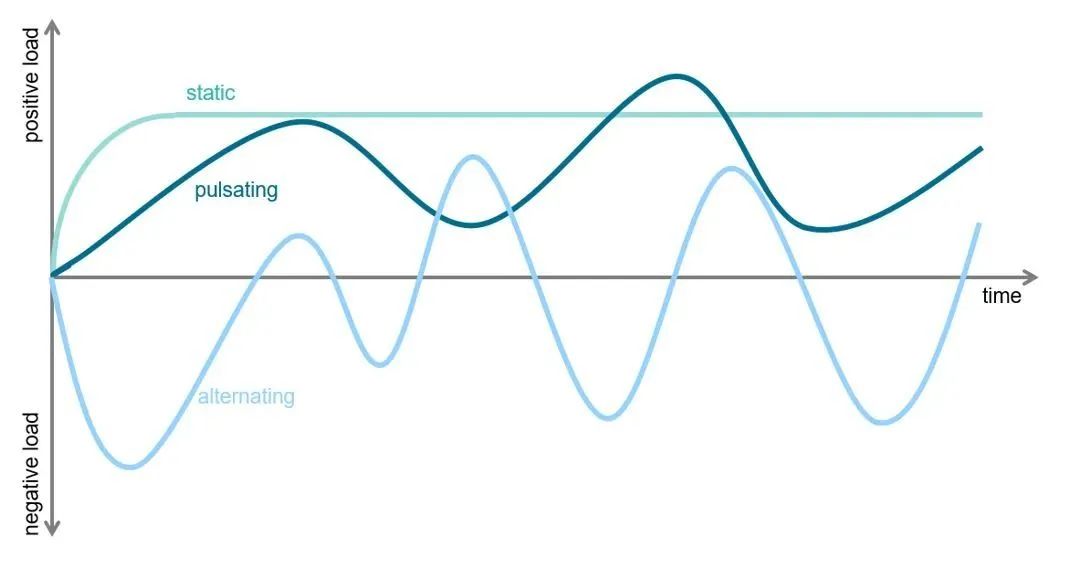
静态与动态、脉动与交变负载
静态负载意味着传感器承受的负载不会随时间变化,也就是说,它是恒定的。另一方面,动态载荷意味着载荷随时间而变化,也就是说,它不是恒定的。在许多应用中,静载荷涉及施加和移除载荷的过程。在达到静载荷之前,载荷会动态增加,当载荷被移除时,载荷会再次动态减少。通常,这些应用程序可以被认为是纯静态的,如有疑问的话,也可以将负载的施加和移除视为单独的动态负载情况。
Static load means that the load on the sensor does not change over time, that is, it is constant. Dynamic loading, on the other hand, means that the load changes over time, that is, it is not constant. In many applications, static loads involve the process of applying and removing loads. The load increases dynamically before the static load is reached and dynamically decreases again when the load is removed. In general, these applications can be considered purely static or, if in doubt, the application and removal of loads can be treated as separate dynamic load cases.
动态载荷可进一步分为脉动载荷和交变载荷。这里的决定性因素是,在脉动负载下,负载方向不会发生逆转。这意味着,施加在传感器上的压向力或拉力,或是某个方向上的扭力,只有有时更强,有时较弱。另一方面,交变加载意味着拉力和压力或顺时针和逆时针扭矩交替变化。荷载的符号反转也说明了这一点。
Dynamic loads can be further divided into pulsating loads and alternating loads. The decisive factor here is that under pulsating loads, the load direction does not reverse. This means that the compressive or tensile force exerted on the sensor, or the torque force in a certain direction, is only sometimes stronger and sometimes weaker. Alternating loading, on the other hand, means alternating tension and pressure or clockwise and counterclockwise torque. This is also illustrated by the symbolic inversion of the loads.
 额定量程,极限负载,破坏负载
额定量程,极限负载,破坏负载
区分这三个参数并不特别困难,然而必须确保传感器的安全使用。在额定量程内,传感器的技术指标都在保证范围内。对于超过额定量程且范围达到极限负载的负载,无法再保证其满足技术规格。但是,此范围内的负载仍然是允许的,如果不经常发生,则不会损坏传感器。当进一步将载荷增加到极限载荷和断裂载荷之间时,测量体变形会达到永久损坏的程度,传感器无法再用于进一步测量。超过破坏载荷极限的载荷将导致传感器断裂。需要注意的是,这些荷载范围仅适用于单轴和静荷载情况。
Distinguishing between these three parameters is not particularly difficult, but safe use of the sensor must be ensured. Within the rated range, the technical specifications of the sensor are within the guaranteed range. Loads that exceed the rated range and range to the limit load are no longer guaranteed to meet the specifications. However, loads in this range are still permissible and will not damage the sensor if they do not occur frequently. When the load is further increased between the limit load and the breaking load, the measuring body deforms to the point of permanent damage and the sensor can no longer be used for further measurements. Loads that exceed the breaking load limit will cause the sensor to break. It should be noted that these load ranges only apply to single-axis and static load cases.
实际应用
了解完不同类型的载荷、极限和标准后,下面就是如何估计应用中传感器的载荷的问题。以下过程已被证明是可行的:
Now that you know the different types of loads, limits, and standards, here's how to estimate the load on the sensor in your application. The following procedure has been proven to be feasible:
选择额定量程 Select the rated range
在大多数情况下,如果测量的方向是已知的,最大量程即为负载绝对值。
In most cases, if the direction of measurement is known, the maximum range is the absolute value of the load.
确定发生的所有荷载 Determine all loads that occur
每个载荷方向的最大载荷可从应用中出现的最大载荷以及几何布置(扭矩=力x杆臂)中得出。需要注意的是这些不仅作为一个绝对值,还包括符号。这项任务通常很耗时,尤其是对于复杂的设置和相互作用的力。然而,它是可靠评估的基础,因此是必要的。除最大荷载外,其他荷载也可能相关。尤其是当涉及不同类型的负载时。例如,如果最大负载为静态负载,但较小的负载为交变和动态负载,则必须对这两种情况进行调查分析。
The maximum load in each load direction can be derived from the maximum load present in the application as well as the geometric arrangement (torque = force x arm ). It is important to note that these are not only taken as an absolute value, but also as symbols. This task is often time-consuming, especially for complex setups and interacting forces. However, it is the basis for a reliable assessment and is therefore necessary. In addition to the maximum load, other loads may also be relevant. Especially when different types of loads are involved. For example, if the maximum load is static, but the smaller load is alternating and dynamic, you must investigate both cases.
荷载工况的定义 Definition of load cases
通常,并非所有荷载都同时发生。可能存在两个力和一个力矩的常规情况,以及使用不同力开始和停止加载的状况。为了能够单独考虑这些情况,将它们细分为独立的负载情况并单独研究每个负载是有意义的。建议为此创建表格。
As a rule, not all loads occur simultaneously. There may be regular cases of two forces and one moment, as well as cases where loading is started and stopped using different forces. To be able to consider these cases individually, it makes sense to subdivide them into independent load cases and study each load separately. It is recommended to create a table for this.
全面评估 Comprehensive assessment
完成上述步骤后,在理想情况下,创建的表格仅包含各个荷载工况的正向结果。在这个表格中,不仅要注意OK(正常)或not OK(不正常),还要注意确切的结果。这样就很容易看出是否选择了不正确量程的传感器,或者所有结果是否一致。
After completing the above steps, ideally the table created contains only positive results for the individual load cases. In this table, note not only OK or Not OK, but also the exact result. This makes it easy to see if an incorrect sensor has been selected or if all results are consistent.
结论 conclusion
选择和评估多分量传感器并非易事。如果你遵循这个循序渐进的过程,准备一个流程图,这个问题可以很容易地处理,得到一个可靠的结果。
Selecting and evaluating multi-component sensors is not an easy task. If you follow this step-by-step process and prepare a flowchart, this problem can be easily dealt with and a reliable result is obtained.
官方订阅号
合作/投稿/发布 请留言
18001928870
长按识别二维码关注我们
图片:EAGOS独家授权
文字:EAGOS易歌石驻英在员

