
So you’ve launched a new IoT product, perhaps using the IoT framework provided by AWS, Azure, or another major cloud provider, and your devices can now send and receive data from the cloud. Now, how do you process that data to get valuable insights, such as device health telemetry or user behavior tracking? There are a number of different ways to set up data processing infrastructure in the cloud that trade off control and complexity. Serverless architecture is ultimately a software design principle that allows you to build, scale, and run services without managing the infrastructure, and MistyWest is excited about how this “serverless” pattern can enable teams to rapidly build and scale cloud solutions.
To help you understand how applicable this is for IoT product solutions, we’re providing the following overview of the different architecture patterns and when you should consider going serverless for your project.
'Serverless architecture allows you to completely offload managing servers to the cloud providers while you can focus directly on your application code.' -MistyWest Click To TweetUsing a Virtual Machine
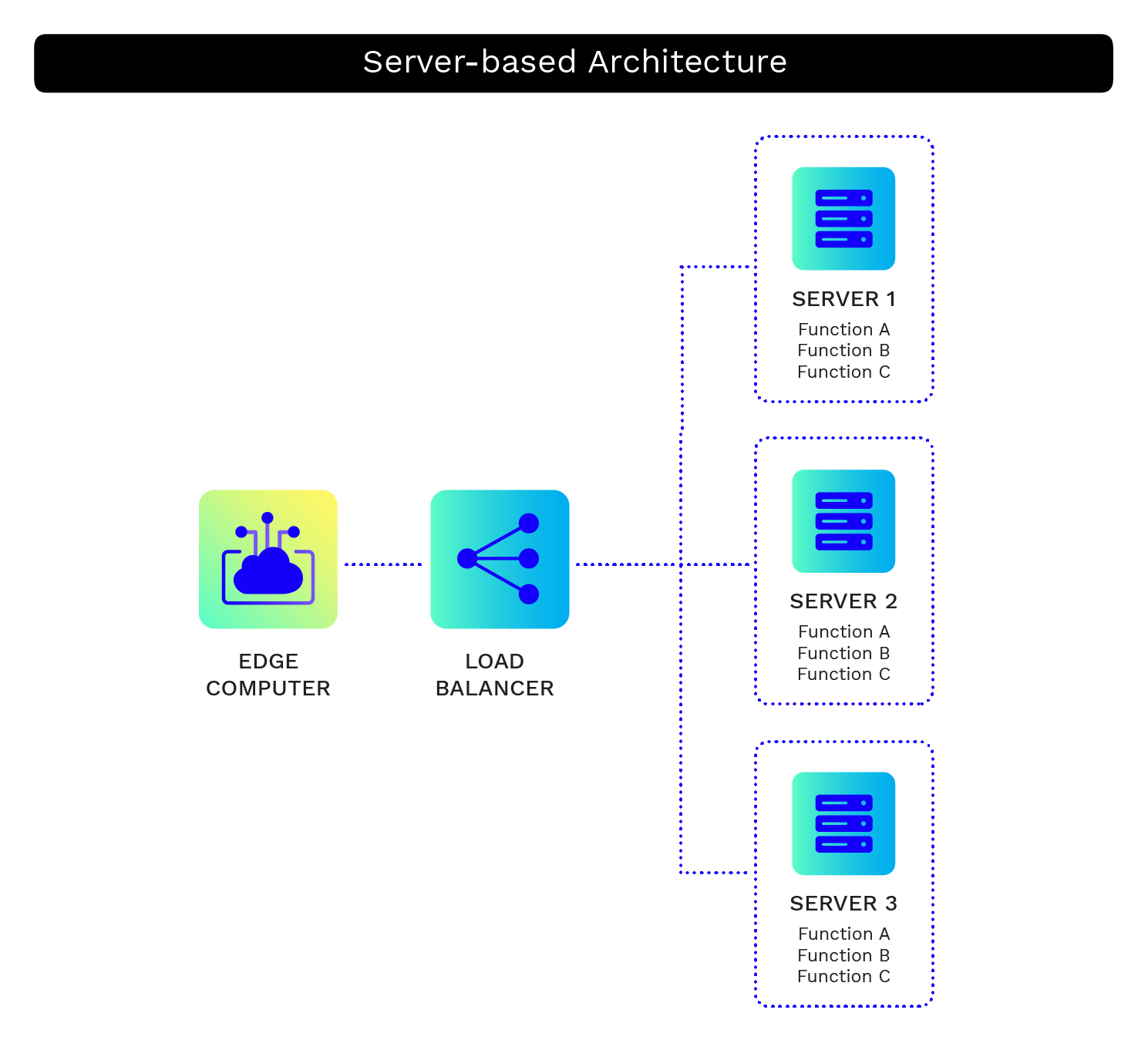
Now, the old-school way of setting up a cloud pipeline, and the recommended way if you want more control, is to spin up a virtual machine (VM) in the cloud to run your processing code. Azure Virtual Machines, AWS EC2, or GCP Compute Engines are some common options. You get a virtual computer that can run code similar to running on your personal computer. However, the limitation of this route is that you will rapidly run out of processing power in a single VM, especially if you’re handling data from thousands of IoT devices.
To get more processing power, you can add more VMs and divide the processing work between many computers. Tools like Kubernetes and Docker Swarm let you orchestrate processing workloads across many machines, and cloud providers offer services like AWS Elastic Kubernetes Service and Google Kubernetes Engine to support orchestrating workloads across multiple machines in the cloud. Services like AWS Elastic Beanstalk or Azure App Services automate the setup and scaling of common web development frameworks like Django, Rails, and Node, and are great starting point services to help you manage them.
Setting up and configuring orchestration tools, however, can be complex, requiring a lot of time and expertise that doesn’t directly provide value for your customers. If you want to prototype quickly to deliver value to your customers and you know that your solution will scale, serverless may be the way to go.
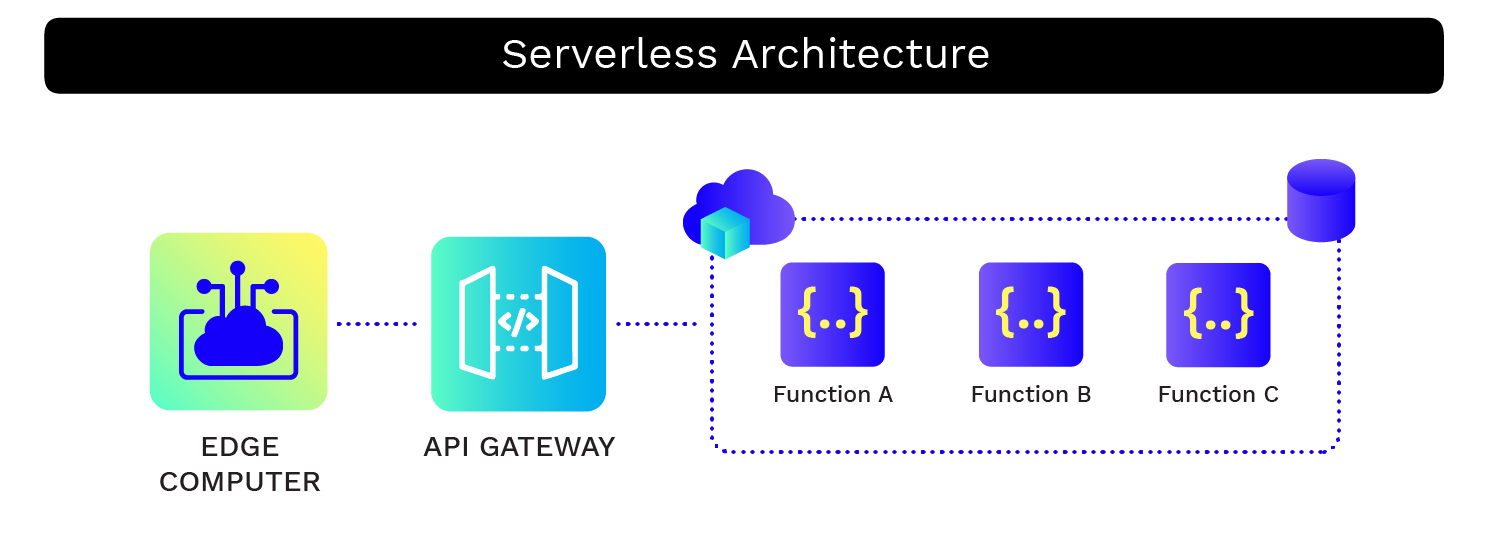
What Is Serverless Architecture?
Serverless architecture allows you to completely offload managing servers to the cloud providers while you can focus directly on your application code. One of the more common architecture subsets is Functions-as-a-Service (FaaS). But serverless architecture provides much more – from databases and queue systems to event processing services, each cloud service provider offers a wide variety to meet your needs.
Benefits of Going Serverless
- Charging: One benefit is that serverless platforms tend to charge based on how often the serverless functions run and for how long, so you only pay for the compute time that you use. This can keep costs low during development while building in a way that automatically scales up during launch.
- Fast Response: Serverless functions also tend to respond quickly to spikes in demand as the platform automatically scales up the amount of compute power available to run the functions, then downscale when the load is reduced. This produces an efficient usage of resources, deploying compute power only when needed.
- Language Options: There is good support for a variety of programming languages, so you can very likely build your serverless functions in your language of choice. For example, AWS Lambda natively supports Java, Go, PowerShell, Node.js, C#, Python, and Ruby, and provides a Runtime API to allow the use of other programming languages. Azure Functions support C#, Javascript, F#, Java, Powershell, Python, and Typescript.
- Bug Prevention: Building with serverless functions necessarily creates a stateless and hostless system, which can simplify reasoning about the system and prevent some complex bugs around state management.
- Data Pipeline: With your IoT framework, you can set up automated, event-driven data pipeline triggers and database storage. By additionally hooking in visualization frameworks or developing your internal dashboard, you can monitor the progress immediately.
- Pay for Less: If you have a VM spun up, you’re paying regardless of whether you’re using the full extent of those resources or if it’s just sitting idle. This isn’t ideal if your IoT device is infrequently sending small packets of data, and even if you have thousands of devices constantly transmitting data, there’s going to be a lot of idle time between packets, which will be quite inefficient. Utilizing a serverless framework allows you to pay only for what you use, and will handle the scaling for you without any configuration change needed – whether you have one device or a million devices. Additionally, if you’re using Azure, as originally proposed in the paper Serverless in the Wild, you’ll be able to dramatically reduce your cold starts by having it predict invocations.
Downfalls of Going Serverless
- Less Control: One downside of using a serverless platform is that you get less fine-grained control of the instance running the code as you don’t have control over the configuration of the underlying hardware. Limits on processing power, memory, and processing time in serverless environments can be a limitation, whereas in a VM you can vertically scale quite heavily.
- Long Latency: One other disadvantage is that because the platform handles scaling up the available compute power (i.e. spinning up more VMs to run functions) during demand spikes, you have less control of the latency that arises when users have to wait for a VM to spin up. This can sometimes cause long latency on the first request, known as “cold start latency” which could be a concern in highly latency-sensitive applications, though isn’t generally an issue.
Elastic Architecture
There are a number of cost comparisons around serverless architecture available on the web; we found Serverless Transformation on Medium and The Burning Monk’s analyses to be very helpful. Serverless architecture is highly applicable to IoT solutions and growing in popularity. With the billions of IoT devices used in the world today, having an elastic architecture is critical for getting to production quickly. Building with a serverless architecture will let you prototype quickly, fail fast, and beat your competition in the long run – just watch out for all of the under-the-hood properties in order to get the most for your buck.
Tweet
Share
Share
- Big Data
- Connectivity
- Consumer IoT
- Cybersecurity
- Data Analytics
- Big Data
- Connectivity
- Consumer IoT
- Cybersecurity
- Data Analytics
